Smol Compiling Firmware
This is the method of compiling firmware if pre-compiled firmware for default pins doesn't fit your needs.
- Required Tools
- Cloning Repositories
- Building Firmware using nRF Connect for VS Code
- Building Firmware Manually (Linux)
- Protocols
- Troubleshooting
- Links
Required Tools
For those interested in building the firmware yourself:
- Git Client
- nRF Connect for Desktop with various integrated tools:
- Programmer (for flashing Nordic and eByte Dongles only)
- Serial Terminal (for sending commands to your Receiver/Trackers, see alternatives)
- Toolchain Manager (for automatic setup of the toolchain for building firmware)
- 2.9.0 (Inside Toolchain Manager) Do not use a newer version!
- NOTE: Installing the Segger J-Link is not necessary for pre-defined boards.
- VS Code (For development purposes only)
- nRF Connect for VS Code (Recommended)
- Install within VS Code extension tab, see the video tutorial
- You may either install the extension itself or the extension pack for additional development tools
- You may also set up a manual build environment in VS Code as the extension is known to fail on some certain Linux distributions.
- nRF Connect for VS Code (Recommended)
- SlimeVR Server
- 0.13.2 or later version
Cloning Repositories
- Open the Command Prompt by typing
cmdin the Start Menu. - Navigate to the directory where you want to clone the repositories.. (Type "cd" followed by a space and then the full path to the desired folder or drive.)
- Cloning SlimeNRF Receiver Repository.
git clone --single-branch --recurse-submodules -b master https://github.com/SlimeVR/SlimeVR-Tracker-nRF-Receiver.git
- Cloning the SlimeNRF Tracker Repository.
git clone --single-branch --recurse-submodules -b master https://github.com/SlimeVR/SlimeVR-Tracker-nRF.git
If you're using an existing case design, you can opt for prebuilt firmware; otherwise, build your own. See Smol Firmware for more details.
Note: It is recommended to clone to a file path that does not contain whitespace or Unicode characters. You may encounter errors when building the firmware.
Building Firmware using nRF Connect for VS Code
Bug Fix for Zephyr 2.9.0
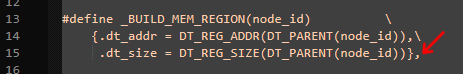
- Open
C:\ncs\v2.9.0\zephyr\drivers\retained_mem\retained_mem_nrf_ram_ctrl.cin your preferred code editor. - Add a comma at the end of Line 15.
- Save the file.
- Launch VS Code using the nRF Connect's Toolchain Manager.
- Open the folder for one of the repositories.
- Make any pin changes or necessary adjustments to
boards\MANUFACTURER\BOARD_NAME.dts. - Click on the nRF Connect tab located on the left side of your screen, approximately halfway down.
- Under "Applications" , click on "+ Add build configuration."
- Select a preset from the "Board Target".
- Scroll down and click the "Build Configuration" button.
Note: For trackers, settings can be found in the "nRF Kconfig GUI" under "Actions" and expand the "SlimeNRF" section.
Changing Board Defines
Board defines can be found in \boards\ for overlays (Boards within the Zephyr library), while custom boards are located in boards\MANUFACTURER\BOARD_NAME.dts.
- Navigate to the board's .dts file.
- The I2C (SCL/SDA) lines can be assigned to different pins. Ensure that you are using "High Frequency" pins and that you change the pins for both lines accordingly.
- SW0 can be ✅ by uncommenting (removing the
//) from the lines below the description comment. If you are using VS Code, you can select the lines and press Ctrl / if you are using VS Code. Additionally, redefine the GPIO pin if necessary. - The INT (int0-gpios) can be redefined in the Zephyr user section.
- The CLK (clk-gpios) can be uncommented and redefined if you are using an IMU with an external clock or crystal oscillator, such as the ICM-42688 or ICM-45686.
Adjusting settings in the Kconfig
- Navigate to the nRF Connect tab of VS Code.
- Build the desired board once.
- A section titled Actions should be displayed on the left navigation panel.
- Select your built board under Applications, then scroll down to the Actions section.
- Double-click nRF Kconfig GUI.
- Scroll down to the SlimeNRF section.
- Enable or disable any necessary configurations, or adjust them as needed.
- Click the "Apply" button, then click the "Save to File" button.
- If prompted to select a file to save, choose prj.conf.
- Click the "Pristine Build" button located next to Build in the Actions section.
Building Firmware Manually (Linux)
This is only recommended if you are experiencing issues with nRF Connect for Desktops Toolchain Manager or nRF Connect for VS Code, as you will need to manually set up the toolchain.
Setup Python Venv
Using a virtual environment (venv) will keep all build tools for Zephyr, such as west, contained.
python3 -m venv ~/.venv/nrf52
source ~/.venv/nrf52/bin/activate (Run the setup whenever you use or modify it.)
pip3 install west
Setup nRF Connect SDK code
Please select an appropriate folder for installing the toolchain, such as ~/.toolchain-nrf52.
Then execute:
west init -m https://github.com/nrfconnect/sdk-nrf --mr v2.9.0 nrf52-sdk-2.9.0
cd nrf52-sdk-2.9.0
west update (This will download dozens of Git repositories; it may take some time.)
pip install -r zephyr/scripts/requirements-base.txt (Install the remaining requirements for building.)
west zephyr-export (This will register the necessary CMake files in your home directory.)
If you move this folder, you simply need to re-run the last command.
Setup Zephyr SDK
The nRF Connect SDK depends on the Zephyr SDK, so please return to your toolchain folder (e.g. ~/.toolchain-nrf52) to install it:
wget -q https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/sdk-ng/releases/download/v0.17.0/zephyr-sdk-0.17.0_linux-x86_64_minimal.tar.xz
tar xf zephyr-sdk-0.17.0_linux-x86_64_minimal.tar.xz -C .
cd zephyr-sdk-0.17.0
./setup.sh -c -t arm-zephyr-eabi (This will register the necessary CMake files in your home directory.)
If you move this folder, you simply need to re-run the last command.
Compiling Manually
Assuming your toolchain is installed in ~/.toolchain-nrf52 and you are in the firmware directory:
source ~/.venv/nrf52/bin/activate
source ~/.toolchain-nrf52/nrf52-sdk-2.9.0/zephyr/zephyr-env.sh
west build --board BOARD --build-dir build . -- -DNCS_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=NONE -DBOARD_ROOT=.
Replace BOARD with your specific board (e.g. supermini_uf2/nrf52840 for the SuperMini, nrf52840dongle/nrf52840 for a dongle receiver).
The compiled firmware will be located at PROJECT_DIR/build/PROJECT_DIR/zephyr/zephyr[.hex|.uf2].
Compiling with VS Code (Without Extensions)
Assuming your toolchain is installed in ~/.toolchain-nrf52, use the following tasks, which should be placed in .vscode/tasks.json:
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Build",
"type": "shell",
"group": "build",
"command": "source",
"args": [
"~/.venv/nrf52/bin/activate", "&&",
"source", "~/.toolchain-nrf52/nrf52-sdk-2.9.0/zephyr/zephyr-env.sh", "&&",
"west", "build", "--board", "BOARD", "--build-dir", "build",
"${workspaceFolder}", "--",
"-DNCS_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=NONE", "-DBOARD_ROOT=${workspaceFolder}"
]
},
]
}
Replace BOARD with your specific board (e.g. supermini_uf2/nrf52840 for the SuperMini, nrf52840dongle/nrf52840 for a dongle receiver).
The compiled firmware will be located at PROJECT_DIR/build/PROJECT_DIR/zephyr/zephyr[.hex|.uf2].
Protocols
This section offers advanced information about the communication protocol and is not necessary for building your own smol slimes.
HID Protocol
The HID Protocol is not finalized and is subject to change in future versions of the SlimeVR Server.
Tracker -> Server
type |id |packet data |
0 |id |proto |batt |batt_v |temp |brd_id |mcu_id |imu_id |mag_id |fw_date |major |minor |patch |rssi | info
1 |id |q0 |q1 |q2 |q3 |a0 |a1 |a2 | full precision quat
2 |id |batt |batt_v |temp |q_buf |a0 |a1 |a2 |rssi | reduced precision quat
3 |id |svr_stat|status |resv |rssi | status
Tracker <-> Receiver
type |id |packet data |
64 |id |addr |resv | pairing data from tracker
65 |id |addr |addr_rcv |channel |resv | pairing data to tracker
66 |id |addr |time | timing data to tracker (why addr?)
67 |id |addr |cmd_data | some command to tracker? (need to be part of timing?)
Tracker <-> Server
type |id |packet data |
128 |id |addr |cmd_data | some command to tracker? (field too large?)
128 |id |addr |ack | acknowledge?
Receiver <-> Server
type |id |packet data |
192 |id |resv | 192+ should be some interaction b/w receiver and server
254 |resv | filler, this packet is ignored by the server
255 |id |addr |resv | tracker id association
Troubleshooting
Please open a GitHub issue for any firmware bugs or issues in the corresponding repositories.
Check Console Logs
- Launch nRF Connect for Desktop.
- Open the Serial Terminal in nRF Connect.
- Ensure that your tracker is connected to your computer using a cable.
- In the top left corner, select your tracker under Devices.
- Click the "Connect to Port" button.
Improving Logging
-
In order to change the log level you see (e.g., LOG_DBG instead of just LOG_INF), you may need to edit the
LOG_MODULE_REGISTERmacro at the top of the relevant module or file you are interested in and then recompile the firmware. -
If you need to view the logs prior to connecting to the serial console, you may need to explicitly initiate the logging backend by adding the following code snippet in the main function of main.c:
const struct log_backend *backend = log_backend_get_by_name("log_backend_uart"); log_backend_enable(backend, backend->cb->ctx, CONFIG_LOG_MAX_LEVEL);Additionally, add the following include to the top of the main.c file:
#include <zephyr/logging/log_ctrl.h> -
If you notice that the logs are truncated at a certain point, the buffer size may be insufficient. This issue has not been fully resolved yet, as simply increasing
CONFIG_LOG_BUFFER_SIZEinprj.confdoes not appear to be effective.
SWD Debugging
- Instructions for the Raspberry Pi, Raspberry Pi Pico, ST-Link V2, and other debuggers will be added in the future. Resource: https://github.com/joric/nrfmicro/wiki/Bootloader
J-Link, nRF52/nRF52840 Development Kit, and OB-ARM Debugger
- Install J-Link Software and Documentation Pack: https://www.segger.com/downloads/jlink/#J-LinkSoftwareAndDocumentationPack
- Download Bootloader HEX File for your device (SuperMini -
nice_nano_bootloader-x.x.x_sxxx_x.x.x.hex, XIAO -xiao_nrf52840_ble_sense_bootloader-x.x.x_sxxx_x.x.x.hex): https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_nRF52_Bootloader/releases - Connect Debugger to SWD IO, CLK, and GND Pins. (It is safer to power up your device by plugging into USB instead of using the VDD pin)
Flashing/Fixing bricked bootloader
- Launch "J-Flash Lite."
- Target Device: NRF52840_XXAA
- Target Interface: SWD
- Speed: 4000
- Click the "OK" button.
- Click on the "..." button and select the downloaded HEX file.
- Click the "Program Device" button.
RTT/Debugging
- Launch "RTT Viewer."
- Connection to J-Link: USB
- Specify Target Device: NRF52840_XXAA
- Force go on connect: Checked
- Target Interface & Speed: SWD / 4000 hKz
- RTT Control Block: Auto Detect
- Click the "OK" button.
Recommended Hardware/Tools
OB-ARM Debugger: https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256806507382540.html
Pogo Pin Test Clip (1.5mm Pitch, 4P, Single Row): https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256805646654844.html
Note: This clip is designed exclusively for SuperMini. While there are less expensive clips available, they do not convert the pins from a 1.5mm pitch to a 2.54mm pitch suitable for Dupont wires.
Links
Firmware Source Code
Community Firmware
| Name | Author | Description | Links |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stacked-SmolSlime | LyallUlric | Fork of main branch with firmware tailored for stacked SuperMini trackers. | Github |